The little project that demonstrate how to implement a path finding in the board game.
respository: https://github.com/CSaratakij/BoardGamePathFinding
responsible: all
Showcase
Demo
Custom Editor
Introduction
My friend love Dokapon, he want to create his own spin for this game.
So, he ask me about the topic he need to research to make it possible.

After I give him a list he need to study, the graph theory is the one I give him.
Sometime pass, he got stuck on how Dokapon path finding works.
(Which need graph theory to better understand the issue. And yes, he do the homework)
After pair programming done, I decide to implement my own just for fun.
How it works
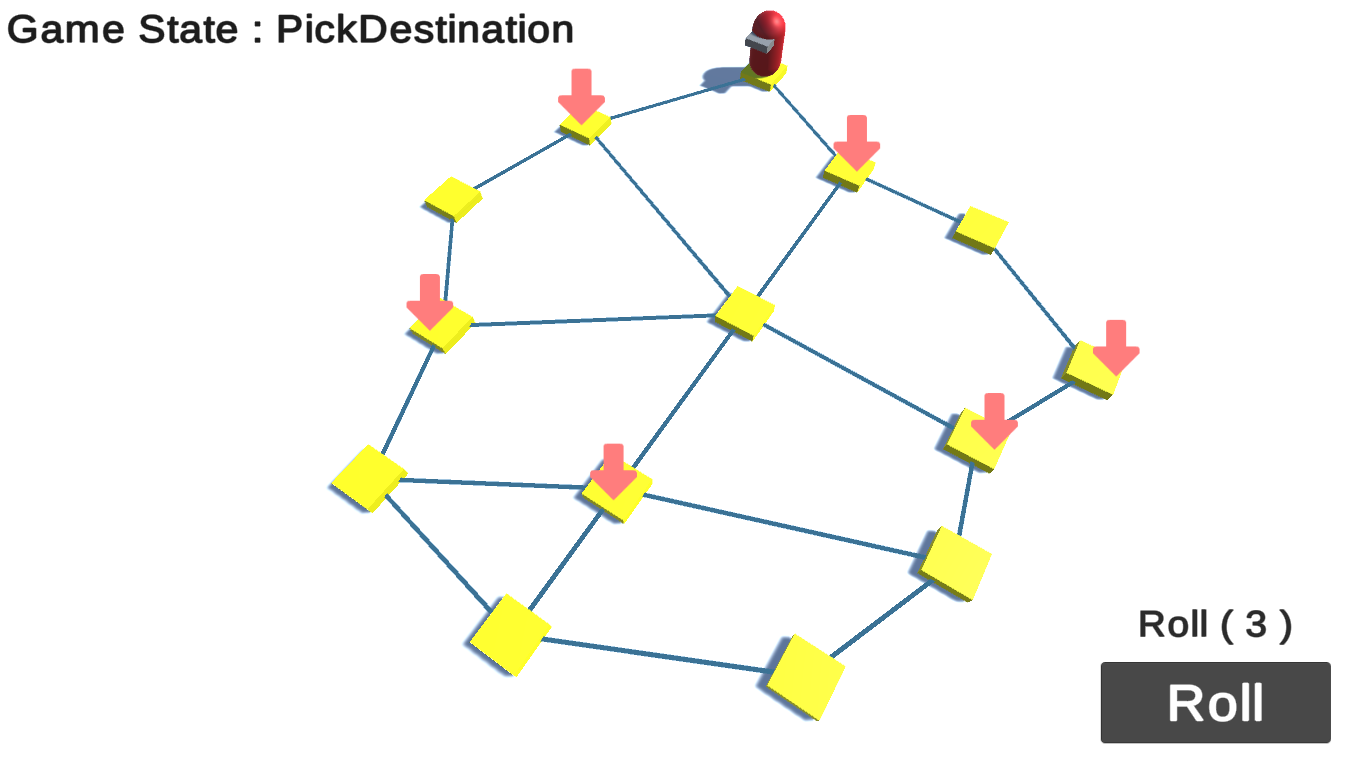
When playing Dokapon, player can see which destination they will reach after roll a dice.
That’s why the game need to know which path reach to the show destination.
Dokapon board is an undirected graph that have the same weight in every edges.
The problem here is not to find the shortest path.
The problem is actually, given N step to travel between node, which paths are availables?
Since the graph has a loop in it, I need to turn it to tree first.
This is what I need to do to find the path.
- From some specific node, turn the graph to the tree by traverse to node in N step.
- Collect node to form the path along the way.
- After having a tree, traverse from leaf to root node and reverse its order to have a complete path.
Technical Challenge
Ofcourse, path finding is challege to implement.
I never play Dokapon, having friend to explain how player see the game work during playthough make problem easier.
Manually testing stuff to check if the algorithm is working or not is error prone and tire some.
A bunch of unit test work great in this scenario.
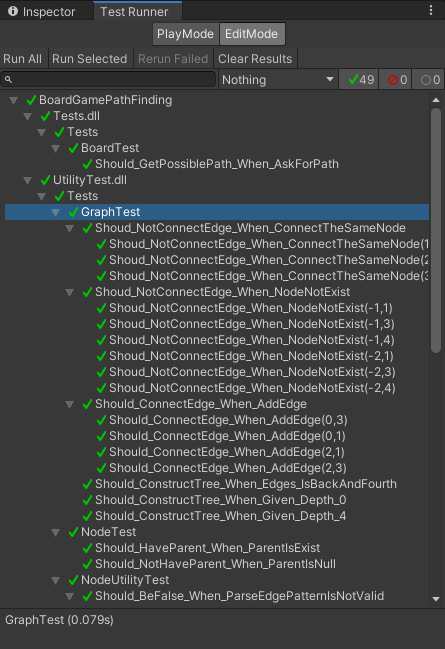
To make this problem easier, I draw the graph and the step to solve this issue.
Let’s me demonstrate.
Path Finding Implementation
Let’s assume the graph look like this.
The edges store by using adjacency list.
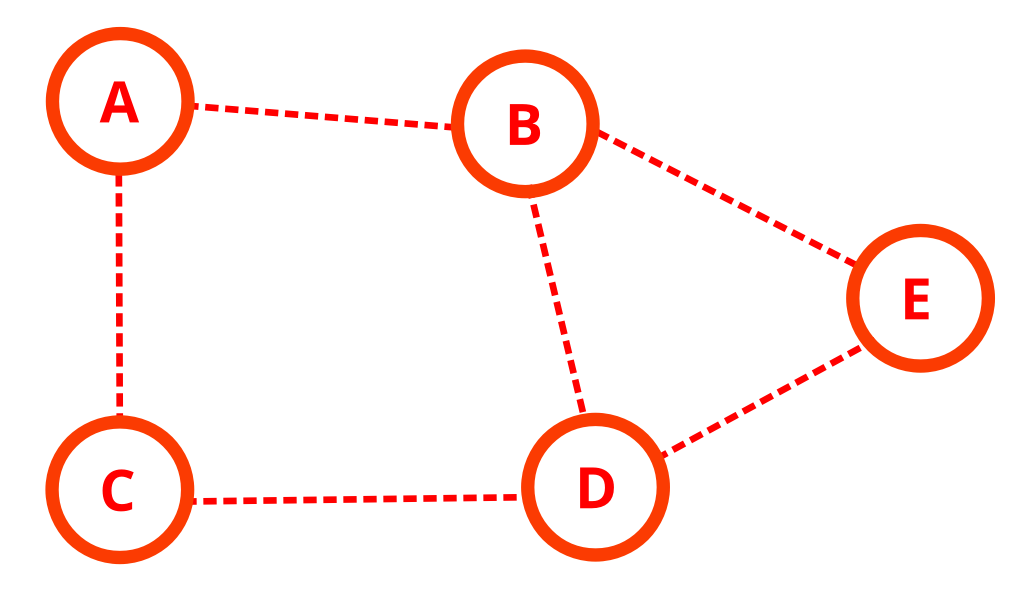
Assume, player current node is at the ‘A’ node.
That’s make ‘A’ node the root of tree.
Let’s say, player roll result is 2.
Then, it need to traverse 2 step from the ‘A’' node.
Using depth first search (DFS) to turn the graph to the tree.
The result look like this.
Tree depth represent the step of node traversal.
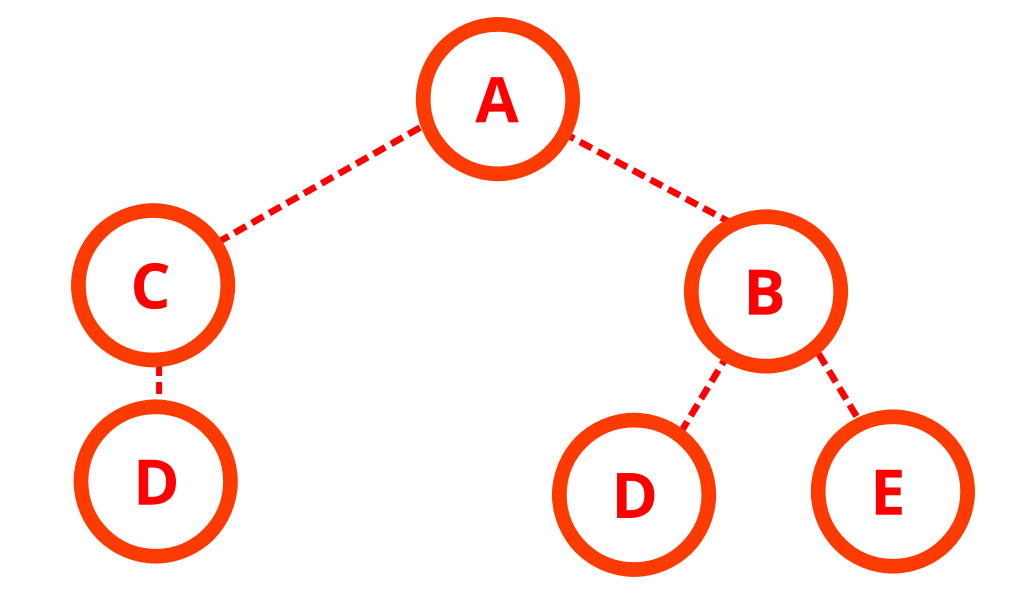
After that, to get the path, we just need to traverse from the leaf node to the root.
Then reverse its order.
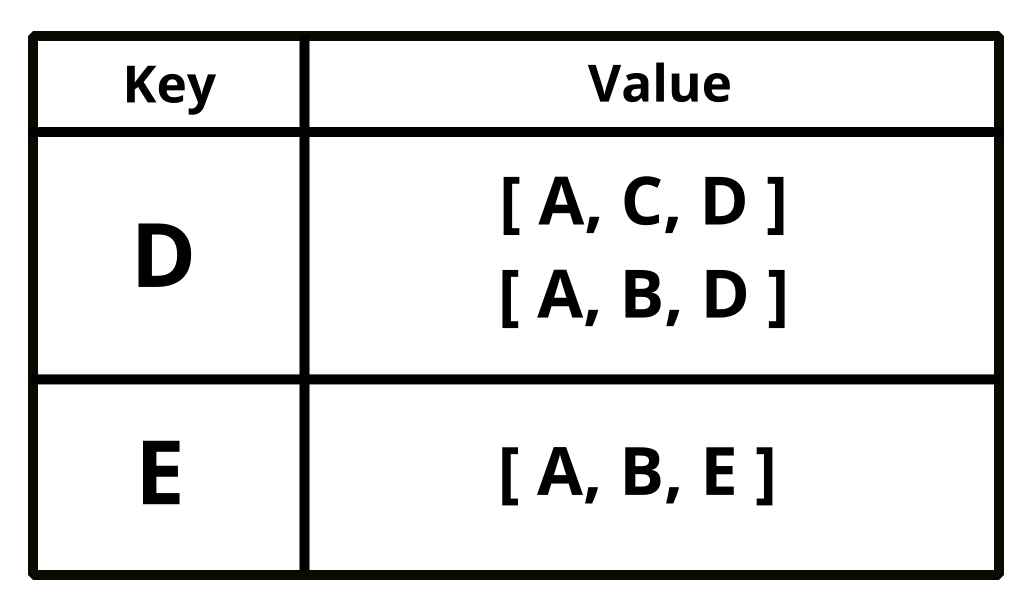
The result store by dictionary (key pair), where key is the destination and value is the path.
(Path can be more than one per destination)
Sometime, depends on the start node.
The path length will be less than the N step, That’s why some path from the tree need to remove.
The reason is simple.
If you roll the dice to get N step, you expect to move by N.
(Not moving less than that)
Summary
Yeah, this is a little fun side project.
With a proper data structure, solving this become possible.